Getting Amazon Reviews for Library Books with Python
26 Feb 2015Often when I want to read about a new technical subject, I’ll see what’s available for free at the local library before buying a new book. To decide which book to check out, I browse through the library’s catalogue and look up the reviews for each book on Amazon to see which book is the best rated. Of course, doing this manually is tedious and repetitive which is usually a sign that it should be automated.
In this post I’ll go over a script I developed that queries a library catalogue for books on a particular subject and then returns the books sorted according to their Amazon rating.
Overview
My local library uses SirsiDynix for its catalogue software. Here’s a screenshot of their advanced search page:
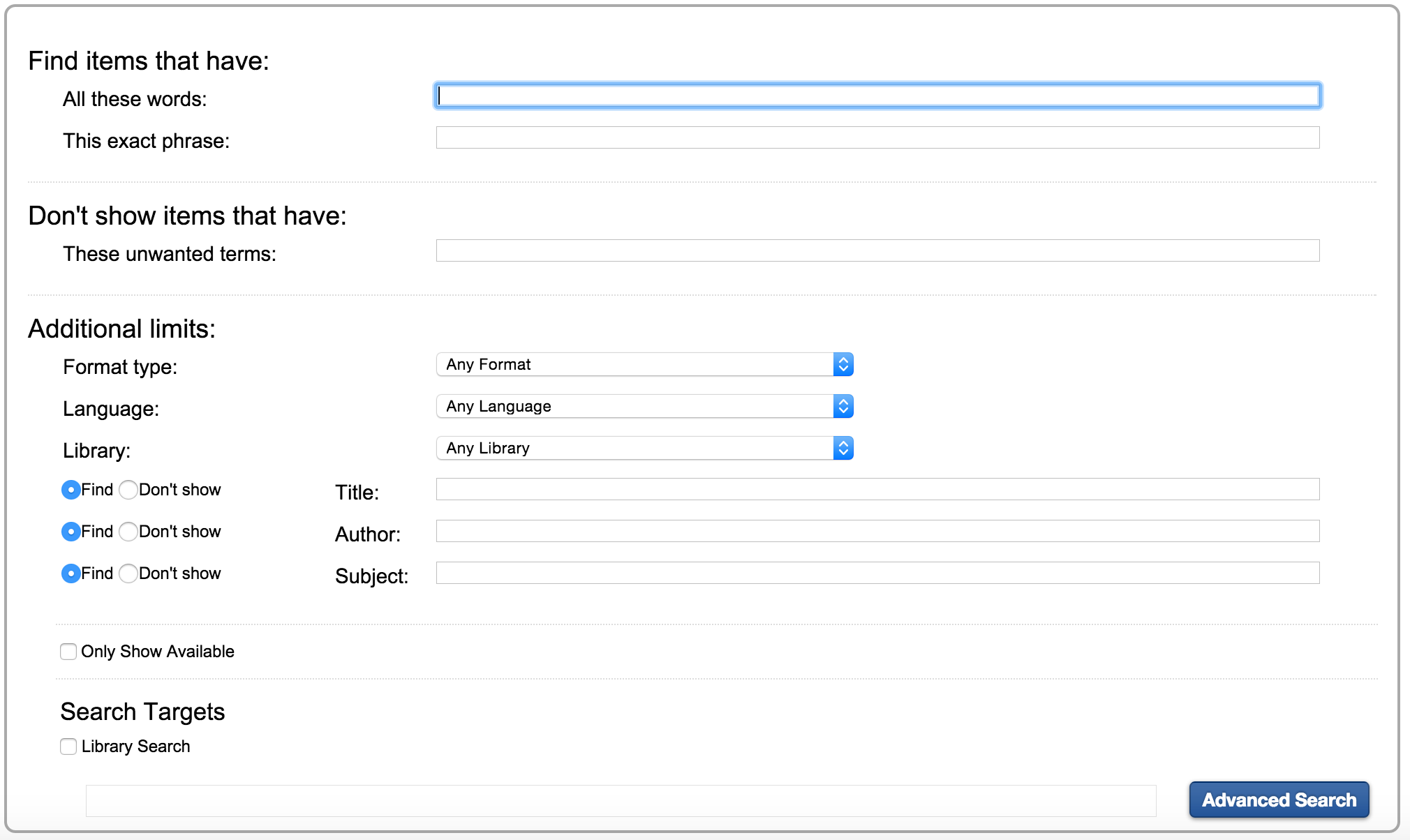
As you can see, searches can be filtered by format type (Electronic Resources, Sound Recording, Books, etc.) and language. For our purposes we only want English language books. Once you submit the search, you get a results page like the following:
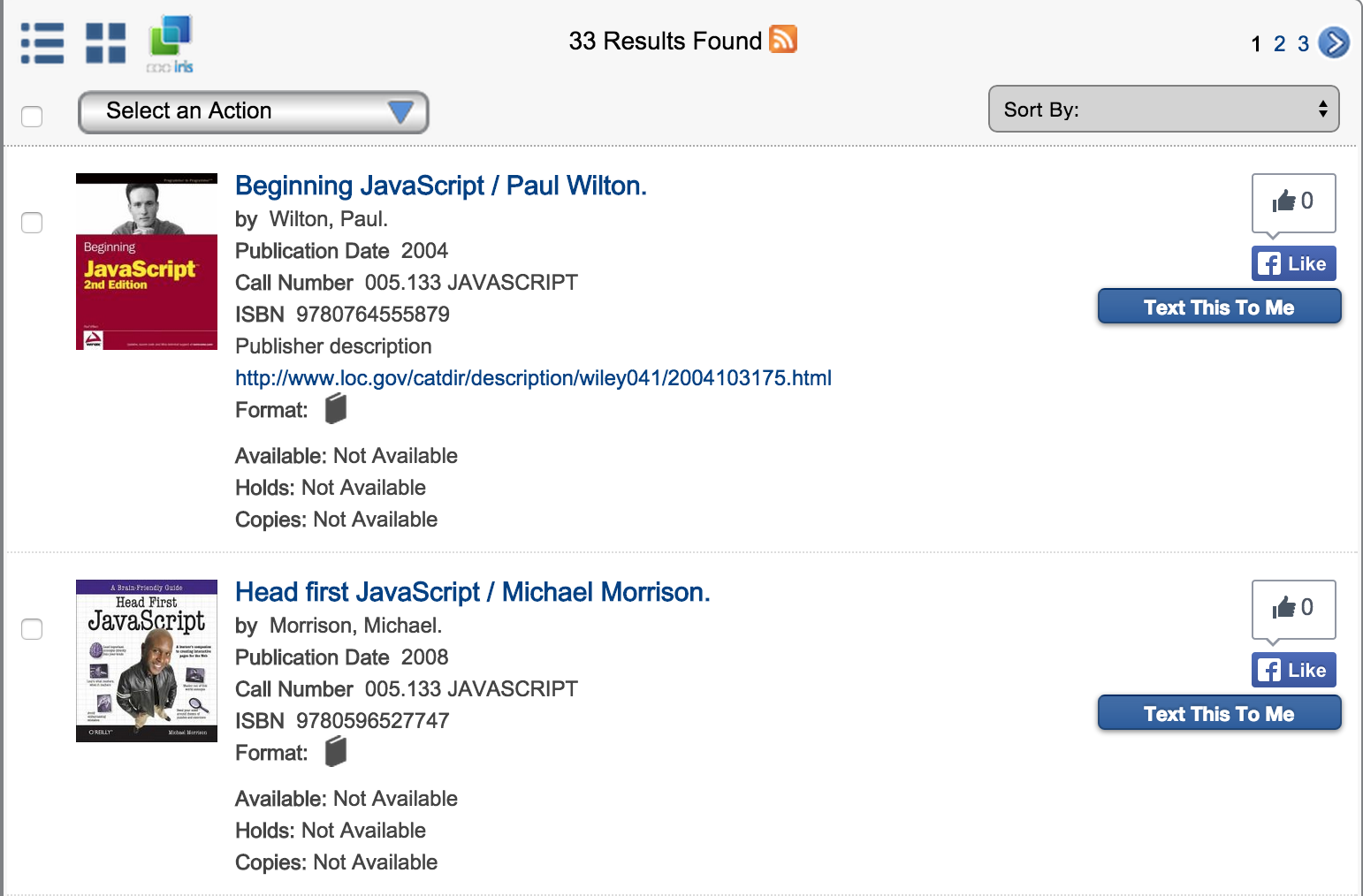
What part of the results do we need to scrape? Well, we’d like the title obviously, and also the book’s ISBN number so we can look it up on Amazon to get its rating. Since results are sorted by relevance we’ll limit our scrape to the first page of results.
Here’s a summary of everything we’ll need the script to do:
- Query the Sirsi catalogue for books on a particular subject
- Scrape the book title and ISBN number for the first page of results
- Use the ISBN number to get the Amazon page for each book
- Scrape the rating for each book from its Amazon page
- Sort the books in reverse order by their Amazon rating
Implementation
We’ll use Mechanize to send our requests and BeautifulSoup to parse the HTML. The script will take two arguments. One argument to specify the url of the advanced search page and the other to specify the search string.
#!/usr/bin/env python
import re
import argparse
import mechanize
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
AMAZON_URL = 'http://www.amazon.com/gp/product/'
class Scraper(object):
def __init__(self):
self.br = mechanize.Browser()
self.br.set_handle_robots(False)
self.br.addheaders = [('User-agent',
'Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_6_8) AppleWebKit/535.7 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/16.0.912.63 Safari/535.7')]
if __name__ == '__main__':
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument("-u", "--url", help="Url", required=True)
parser.add_argument("-q", "--query", help="Query", required=True)
args = parser.parse_args()
scraper = Scraper()
scraper.scrape(args.url, args.query)
A top level scrape() method encapsulates all of the logic.
def scrape(self, url, q):
books = self.search_library_books(url=url, q=q)
self.get_amazon_reviews(books)
books = self.rank_by_reviews(books)
for b in books:
print b['rating'], b['title']
Scraping the Library Catalogue
To scrape the book titles and ISBN numbers from the Sirsi catalogue, we open up the advanced search page,
fill out and submit the form. The search results are then filtered based on the class and id attributes
of the elements containing the title and ISBN number.
def search_library_books(self, url, q):
'''
Scrape the first page of books for the given query.
Calculate the ISBN10 value for each book so we can
look it up on Amazon
'''
books = []
def select_form(form):
return form.attrs.get('id', None) == 'advancedSearchForm'
self.br.open(url)
self.br.select_form(predicate=select_form)
self.br.form['allWordsField'] = q
self.br.form['formatTypeDropDown'] = ['BOOK']
self.br.form['languageDropDown'] = ['ENG']
self.br.submit()
s = BeautifulSoup(self.br.response().read())
x = {'class': 'isbnValue'}
y = re.compile(r'^results_cell\d+$')
z = re.compile(r'^results_bio\d+$')
for i in s.findAll('input', attrs=x):
d = i.findParent('div', id=y)
d = d.find('div', id=z)
if not i.get('value'):
continue
book = {}
book['title'] = d.a['title']
book['isbn13'] = i['value']
book['isbn10'] = self.isbn13to10(book['isbn13'])
books.append(book)
return books
Note that we scrape the ISBN13 number and then convert it to ISBN10. That’s because while the Sirsi catalogue uses ISBN13 numbers, Amazon uses ISBN10 numbers for product links. [1] [2]
ISBN13 to ISBN10 Conversion
Wikipedia has a nice writeup on how ISBN numbers are formatted. To convert an ISBN13 number to ISBN10, we chop off the first 3 digits of the ISBN13 number, then calculate the ISBN10 check digit for the next nine numbers. The nine numbers plus the check digit is the ISBN10 number.
def isbn13to10(self, isbn13):
'''
Convert an ISBN13 number to ISBN10 by chomping off the
first 3 digits, then calculating the ISBN10 check digit
for the next nine digits to come up with the ISBN10
'''
first9 = isbn13[3:][:9]
isbn10 = first9 + self.isbn10_check_digit(first9)
return isbn10
The formula for calculating an ISBN10 check digit (the 10th number) given the first nine numbers is as follows:
(11 - ((10x1 + 9x2 + 8x3 + 7x4 + 6x5 + 5x6 + 4x7 + 3x8 + 2x9) mod 11)) mod 11
def isbn10_check_digit(self, isbn10):
'''
Given the first 9 digits of an ISBN10 number calculate
the final (10th) check digit
'''
i = 0
s = 0
for n in xrange(10,1,-1):
s += n * int(isbn10[i])
i += 1
s = s % 11
s = 11 - s
v = s % 11
if v == 10:
return 'x'
else:
return str(v)
Amazon Reviews
Once we’ve got the ISBN10 number for the book, we can look it up on Amazon using the following link format:
http://www.amazon.com/gp/product/<ISBN10>
Then we can go to that page and scrape the rating for the book.
def get_amazon_reviews(self, books):
'''
Get the Amazon review/rating for each book in books[]
'''
for b in books:
url = AMAZON_URL + b['isbn10']
self.br.open(url)
s = BeautifulSoup(self.br.response().read())
d = s.find('div', id='avgRating')
m = re.search(r'\d+(\.\d+)?', d.text.strip())
f = float(m.group(0))
b['rating'] = f
Sorting the Results
Once we’ve got all the rating for all of the books, we sort them according to their rating.
def rank_by_reviews(self, books):
'''
Sort books by rating with highest rated books first
'''
newlist = sorted(books, key=lambda k: k['rating'], reverse=True)
return newlist
Running It
Let’s try it out.
$ ./scraper.py -u https://mdpl.ent.sirsi.net/client/catalog/search/advanced -q javascript 4.7 Beginning JavaScript / Paul Wilton. 4.6 JavaScript : the definitive guide / David Flanagan. 4.6 Professional JavaScript for Web developers / Nicholas C. Zakas. 4.5 High performance JavaScript / Nicholas C. Zakas. 4.5 JavaScript : the definitive guide / David Flanagan. 4.3 PPK on JavaScript / Peter-Paul Koch. 4.1 Pure JavaScript / Jason Gilliam, Charlton Ting, R. Allen Wyke. 4.0 JavaScript bible / Danny Goodman, Michael Morrison. 4.0 JavaScript : a beginner's guide / John Pollock. 3.7 JavaScript & Ajax for dummies / Andy Harris. 3.5 Head first JavaScript / Michael Morrison. 2.2 JavaScript for dummies / by Emily A. Vander Veer.
Each result from the library catalogue is printed out along with its Amazon rating, with the highest rated books listed first.
If you’d like to see the full implementation, the source code for this article is available on github.
Shameless Plug
Have a scraping project you’d like done? I’m available for hire. Contact me for a free quote.