Scraping AJAX Pages with Python
11 Mar 2015In this post I’ll show an example of how to scrape AJAX pages with Python.
Overview
Scraping AJAX pages involves more than just manually reviewing the HTML of the page you want to scrape. That’s because an AJAX page uses javascript to make a server request for data that is then dynamically rendered into the current page.
It follows then that to scrape the data being rendered you have to determine the format and endpoint of the request being made so that you can replicate the request, and the format of the response so that you can parse it.
The AJAX page that I’ll show how to scrape in this post is the jobs page for Apple.com.
The scraper I develop in this post uses Requests and BeautifulSoup. I assume you are using the Chrome browser on OSX. For those using other browsers/OS combinations, the concepts remains the same.
Finding the AJAX Request
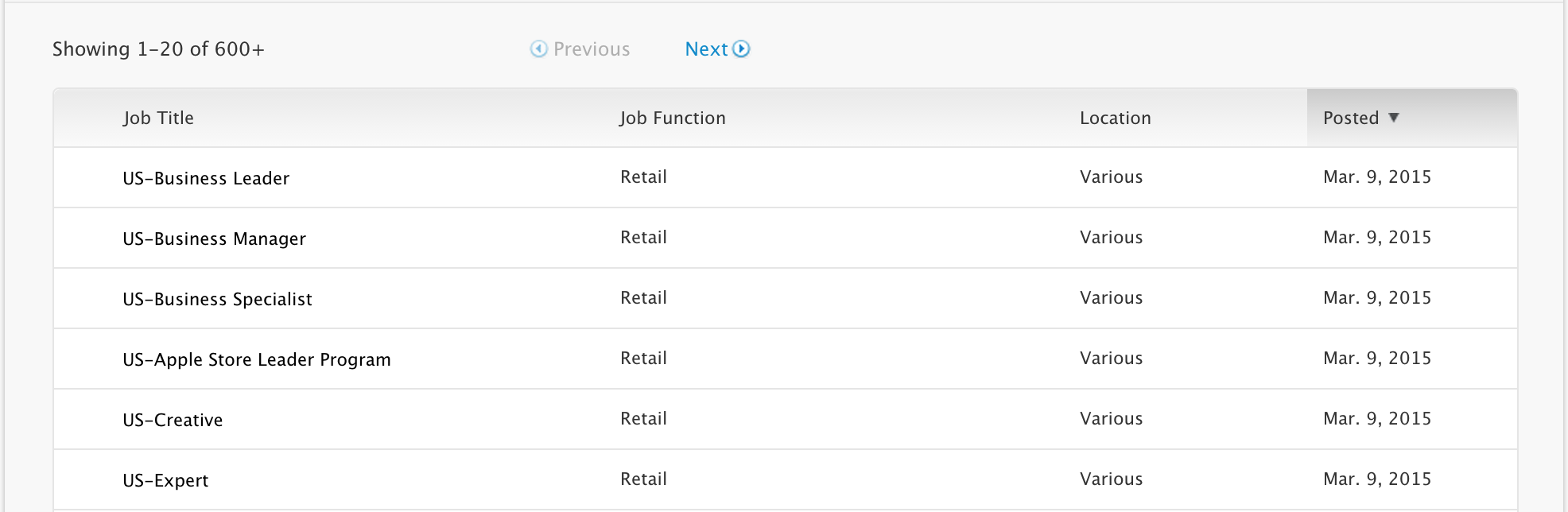
Open the page https://jobs.apple.com/us/search. Scroll down a bit and you’ll see a jobs listing like the following.
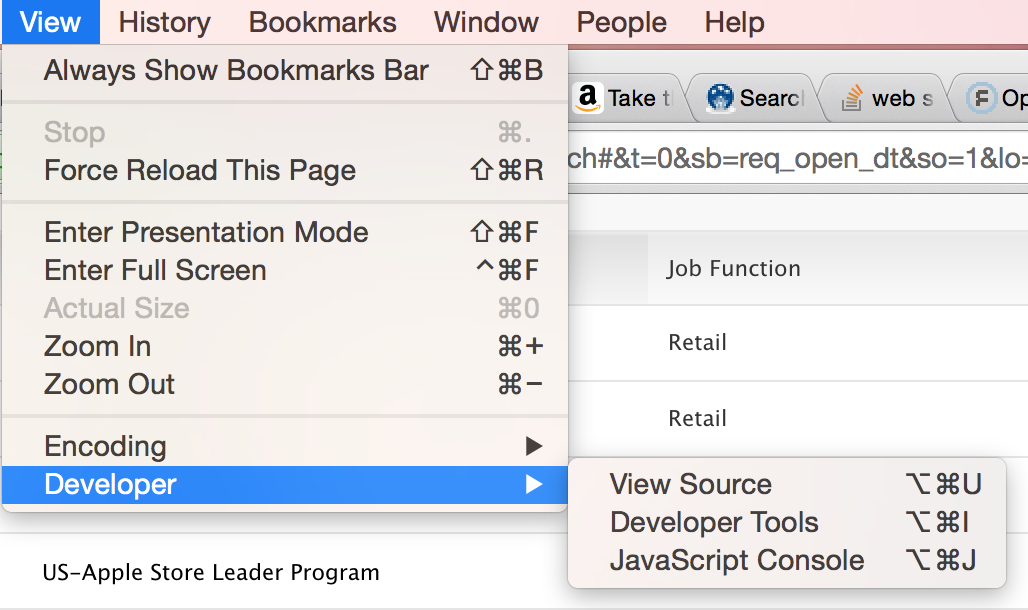
Open the Chrome developer tools by selecting View > Developer > Developer Tools
Your browser screen should split in two with the developer tools window appearing in the bottom half. Select the Network tab.
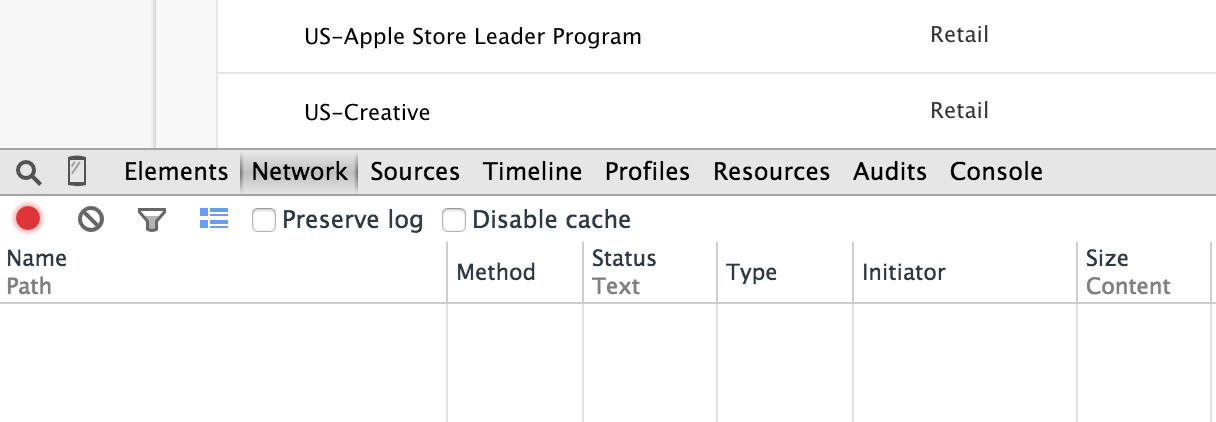
Refresh the page. You should see Network tab fill up with the HTTP requests being made for the Apple jobs page. Scroll down until you see the POST request to search-result.

Click on that line to see the details of that request.
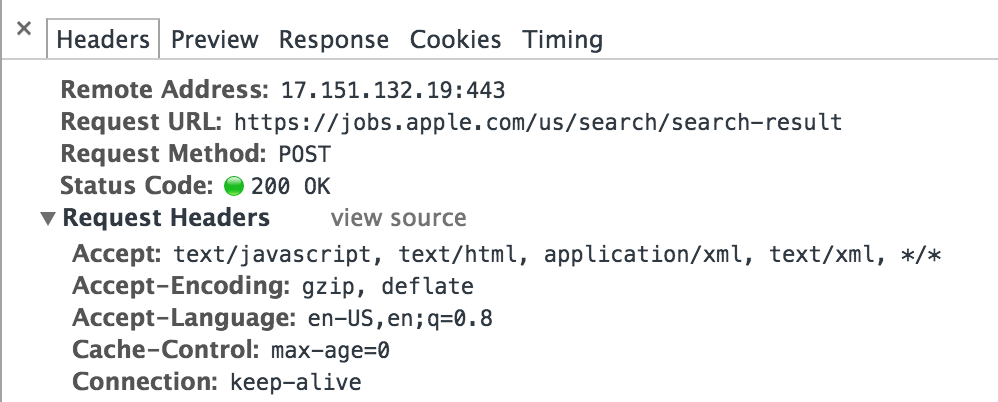
Under the headers tab, scroll down until you see the Form Data.
This is the AJAX request that retrieves the jobs that are rendered on the page. So to scrape jobs from this page, we need to replicate this request. Let’s look at the details of this request.
There are two parameters: searchRequestJson and clientOffset. We’ll send both in our request. The clientOffset
parameter is simple. It’s just set to -300. The searchRequestJson field is more complex. Here’s a formatted listing.
{
"searchString":"",
"jobType":0,
"sortBy":"req_open_dt",
"sortOrder":"1",
"language":null,
"autocomplete":null,
"delta":0,
"numberOfResults":0,
"pageNumber":0,
"internalExternalIndicator":0,
"lastRunDate":0,
"countryLang":null,
"filters":{
"locations":{
"location":[
{
"type":0,
"code":"USA",
"countryCode":null,
"stateCode":null,
"cityCode":null,
"cityName":null
}
]
},
"languageSkills":null,
"jobFunctions":null,
"retailJobSpecs":null,
"businessLine":null,
"hiringManagerId":null
},
"requisitionIds":null
}
The searchRequestionJson parmater is a JSON string whose pageNumber field controls which page of results
is returned for a request. That field will get incremented for each page we retrieve.
Here’s the equivalent Python dictionary. We’ll convert this dict into a JSON string when we send our requests.
{
"searchString":"",
"jobType":0,
"sortBy":"req_open_dt",
"sortOrder":"1",
"language":None,
"autocomplete":None,
"delta":0,
"numberOfResults":0,
"pageNumber":0,
"internalExternalIndicator":0,
"lastRunDate":0,
"countryLang":None,
"filters":{
"locations":{
"location":[{
"type":0,
"code":"USA",
"countryCode":None,
"stateCode":None,
"cityCode":None,
"cityName":None
}]
},
"languageSkills":None,
"jobFunctions":None,
"retailJobSpecs":None,
"businessLine":None,
"hiringManagerId":None
},
"requisitionIds":None
}
Response Format
Next click on the Response tab to see how jobs are returned for a query.

Jobs are returned in XML. If you select the entire response and format the results you’ll get a listing like the following.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
<result>
<count>2557</count>
<requisition>
<jobfunction>Retail</jobfunction>
<jobId>USABL</jobId>
<jobTypeCategory>Retail</jobTypeCategory>
<location>Various</location>
<retailPostingDate>Mar. 7, 2015</retailPostingDate>
<retailPostingTitle>US-Business Leader</retailPostingTitle>
</requisition>
<requisition>
<jobfunction>Retail</jobfunction>
<jobId>USABM</jobId>
<jobTypeCategory>Retail</jobTypeCategory>
<location>Various</location>
<retailPostingDate>Mar. 7, 2015</retailPostingDate>
<retailPostingTitle>US-Business Manager</retailPostingTitle>
</requisition>
...
</result>
For our scraper, we’ll extract the job title, ID, and location for each job in the listing.
Implementing the Scraper
We have enough information now to write our scraper. Before we get started with the code, let’s summarize what we need our scraper to do:
- Construct the
searchRequestJsondictionary. - Initialize
searchRequestJson['pageNumber']to 0. - Convert the
searchRequestJsondict into a JSON string - Send a POST request to
https://jobs.apple.com/us/search/search-resultwithsearchRequestJsonandclientOffsetparameters. - Parse the XML response with BeautifulSoup and extract the job title, id, and location for each job.
- Increment the
pageNumberfield of thesearchRequestJsondict. - Go to step 3 to get the next page of results.
Now let’s write the code.
First, create a class named AppleJobsScraper with a dict named search_request for building the searchRequestJson string.
#!/usr/bin/env python
import json
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
class AppleJobsScraper(object):
def __init__(self):
self.search_request = {
"searchString":"",
"jobType":0,
"sortBy":"req_open_dt",
"sortOrder":"1",
"language":None,
"autocomplete":None,
"delta":0,
"numberOfResults":0,
"pageNumber":None,
"internalExternalIndicator":0,
"lastRunDate":0,
"countryLang":None,
"filters":{
"locations":{
"location":[{
"type":0,
"code":"USA",
"countryCode":None,
"stateCode":None,
"cityCode":None,
"cityName":None
}]
},
"languageSkills":None,
"jobFunctions":None,
"retailJobSpecs":None,
"businessLine":None,
"hiringManagerId":None},
"requisitionIds":None
}
Next, add a method named scrape. It will call scrape_jobs and print out
the list of jobs returned.
def scrape(self):
jobs = self.scrape_jobs()
for job in jobs:
print job
The scrape_jobs method is where we implement the steps discussed earlier.
def scrape_jobs(self, max_pages=3):
jobs = []
pageno = 0
self.search_request['pageNumber'] = pageno
while pageno < max_pages:
payload = {
'searchRequestJson': json.dumps(self.search_request),
'clientOffset': '-300'
}
r = requests.post(
url='https://jobs.apple.com/us/search/search-result',
data=payload,
headers={
'X-Requested-With': 'XMLHttpRequest'
}
)
s = BeautifulSoup(r.text)
if not s.requisition:
break
for r in s.findAll('requisition'):
job = {}
job['jobid'] = r.jobid.text
job['title'] = r.postingtitle and \
r.postingtitle.text or r.retailpostingtitle.text
job['location'] = r.location.text
jobs.append(job)
# Next page
pageno += 1
self.search_request['pageNumber'] = pageno
return jobs
On line 4 we initialize pageNumber to 0 to get the first page of jobs.
Then on lines 7-10 we create a dict for the parameters we’ll be sending in the POST request. We
convert search_request into a JSON string using json.dumps in the process.
Next on lines 12-18 we send the POST request. I’ve included the headers argument to show how you can control what headers are sent in your request, but it’s not necessary in this case to make the request work.
After we’ve sent the request, we parse our response using BeautifulSoup and extract the desired fields.
On lines 33-34 we increment the page and then repeat our previous steps until we’ve gotten max_pages (by default 3) worth of results.
Let’s try it out by instantiating the scraper and calling scrape().
if __name__ == '__main__':
scraper = AppleJobsScraper()
scraper.scrape()
Now run it from the command line:
$ ./scraper.py | head
{'title': u'US-Business Leader', 'location': u'Various', 'jobid': u'USABL'}
{'title': u'US-Business Manager', 'location': u'Various', 'jobid': u'USABM'}
{'title': u'US-Business Specialist', 'location': u'Various', 'jobid': u'USABS'}
{'title': u'US-Apple Store Leader Program', 'location': u'Various', 'jobid': u'USALP'}
{'title': u'US-Creative', 'location': u'Various', 'jobid': u'USACR'}
{'title': u'US-Expert', 'location': u'Various', 'jobid': u'USAEX'}
{'title': u'US-Inventory Specialist', 'location': u'Various', 'jobid': u'USAIS'}
{'title': u'US-Manager', 'location': u'Various', 'jobid': u'USAMN'}
{'title': u'US-Market Leader', 'location': u'Various', 'jobid': u'USAML'}
{'title': u'US-Genius', 'location': u'Various', 'jobid': u'USAGN'}
If you’d like to see the full implementation, the source code for this article is available on github.
Shameless Plug
Have a scraping project you’d like done? I’m available for hire. Contact me for a free quote.
